I was brushing up on my C# knowledge after submitting a resume for a C# programming job because I haven’t done any serious work in it in ten years. I used it to build a tool that would tell me what me L1 and L2 cache sizes are because on a whim I was reading about cache lines and multithreading and learning why C++ developers are constantly blathering on about cache misses when they’re peacocking.
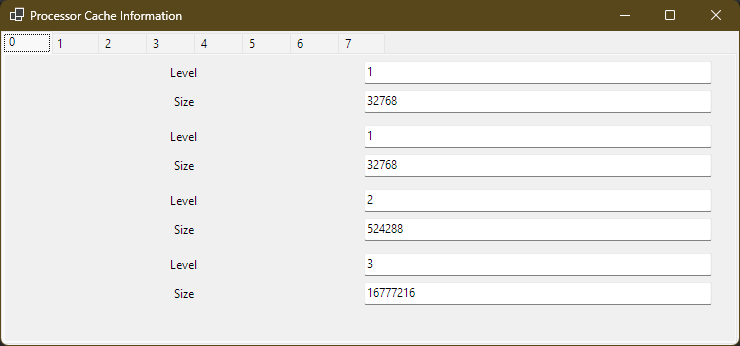
Of course I would choose an obnoxiously difficult API function to marshal. (Marshalling is a big blind spot in my C# skill set.) Thankfully, StackOverflow had my back. Here it is in most of its glory.
Marshall.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6972437/pinvoke-for-getlogicalprocessorinformation-function
namespace LogicalProcessorInformation
{
// [StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)] isn't needed here
// C#, Visual Basic, and C++ compilers apply the Sequential layout value to structures by default.
public struct PROCESSORCORE
{
public byte Flags;
};
public struct NUMANODE
{
public uint NodeNumber;
}
public enum PROCESSOR_CACHE_TYPE
{
CacheUnified,
CacheInstruction,
CacheData,
CacheTrace
}
public struct CACHE_DESCRIPTOR
{
public byte Level;
public byte Associativity;
public ushort LineSize;
public uint Size;
public PROCESSOR_CACHE_TYPE Type;
}
// A union is a structure with an Explicit layout and FieldOffset
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)]
public struct SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION_UNION
{
[FieldOffset(0)] // The [FieldOffset(int offset)] attribute in C# is used to specify the exact physical position, in bytes, of a field within the unmanaged representation of a struct
public PROCESSORCORE ProcessorCore;
[FieldOffset(0)]
public NUMANODE NumaNode;
[FieldOffset(0)]
public CACHE_DESCRIPTOR Cache;
[FieldOffset(0)]
private readonly UInt64 Reserved1;
[FieldOffset(8)]
private readonly UInt64 Reserved2;
}
public enum LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_RELATIONSHIP
{
RelationProcessorCore,
RelationNumaNode,
RelationCache,
RelationProcessorPackage,
RelationGroup,
RelationAll = 0xffff
}
public struct SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION
{
public UIntPtr ProcessorMask;
public LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_RELATIONSHIP Relationship;
public SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION_UNION ProcessorInformation;
}
internal partial class Marshall // internal = accessible only within this assembly
{
// by making a nested class for the native types and functions, I can protect
// access to them despite them needed to be public because of the Marshall object
private class Native
{
[DllImport(@"kernel32.dll",SetLastError=true)]
public static extern bool GetLogicalProcessorInformation(
IntPtr Buffer,
ref uint ReturnLength
);
private const int ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER=122;
public required SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION[] buffer; // by nested this in a private class, I've essentially made this private
[SetsRequiredMembers] // without this, new() in the Marshall() constructor will fail to compile because buffer is marked required and the compiler doesn't know this constructore fulfills that requirement.
public Native()
{
uint size=0;
// GetLastPInvokeError() supersedes GetLastSystemError(): https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.runtime.interopservices.marshal.getlastpinvokeerror?view=net-10.0#remarks
// this call is intended to fail, triggering it to return the required size
if (GetLogicalProcessorInformation(IntPtr.Zero,ref size)) // IntPtr = pointer to a handle
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Failed to obtain required size of memory to allocate");
}
else
{
var errorCode=Marshal.GetLastPInvokeError();
if (errorCode != ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER) throw new Win32Exception(errorCode);
}
unsafe
{
IntPtr memory=(IntPtr)NativeMemory.Alloc(size);
try
{
if (GetLogicalProcessorInformation(memory,ref size))
{
int structSize=Marshal.SizeOf<SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION>();
int count=(int)size/structSize;
buffer=new SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION[count];
IntPtr offset=memory;
for (int index=0; index < count; index++)
{
var candidate=Marshal.PtrToStructure<SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION>(offset);
buffer[index]=(SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION)candidate;
offset+=structSize;
}
}
else
{
throw new Win32Exception();
}
}
finally
{
NativeMemory.Free((void*)memory);
}
}
}
}
private readonly Native native;
public Marshall()
{
native=new(); // see note on SetsRequiredMembers attribute on Native
}
public ref readonly SYSTEM_LOGICAL_PROCESSOR_INFORMATION[] Processors()
{
return ref native.buffer;
}
}
}
Code language: C# (cs)CacheEntry.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace LogicalProcessorInformation
{
public partial class CacheEntry: UserControl
{
public CacheEntry(int level,int size)
{
InitializeComponent();
textLevel.Text=level.ToString();
textSize.Text=size.ToString();
}
private void CacheEntry_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
ClientSize=new Size(ClientSize.Width,textLevel.Height+textSize.Height+Padding.Vertical+textSize.Margin.Vertical+textLevel.Margin.Vertical);
}
}
}
Code language: C# (cs)CacheInformation.cs
using System;
using System.CodeDom;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Diagnostics.Contracts;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using static System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles.VisualStyleElement;
namespace LogicalProcessorInformation
{
public partial class CacheInformation: Form
{
public CacheInformation()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void LogicalProcessorInformation_Load(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
try
{
var marshall=new Marshall();
foreach (var entry in marshall.Processors())
{
// we're only interested in entries with cache information
if (entry.ProcessorInformation.Cache.Level == 0 || entry.ProcessorInformation.Cache.Size == 0) continue;
// mask has a bit set for each logical processor this entry represents
var mask=entry.ProcessorMask;
List<int> CPUs=[];
for (int position=0; position < UIntPtr.Size; position++)
{
if (((int)mask & (1 << position)) != 0) CPUs.Add(position);
}
foreach (var CPU in CPUs) // for each bit that was set above
{
var CPUName=CPU.ToString(); // make the position of the bit our tab text
var page=Listing.TabPages.Cast<TabPage>().FirstOrDefault(tab => tab.Name == CPUName);
FlowLayoutPanel scrollablePanel;
// set up a new page if there isn't one, otherwise use the one we got from LINQ
if (page is null)
{
scrollablePanel=new FlowLayoutPanel
{
Dock=DockStyle.Fill,
FlowDirection=FlowDirection.TopDown,
WrapContents=false,
AutoScroll=true
};
SizeChanged+=new EventHandler(ScrollablePanel_SizeChanged!);
page=new TabPage
{
Name=CPUName,
Dock=DockStyle.Fill,
Text=CPUName
};
page.Controls.Add(scrollablePanel);
Listing.TabPages.Add(page);
}
else
{
scrollablePanel=page.Controls.OfType<FlowLayoutPanel>().First();
}
CacheEntry entryForm=new (entry.ProcessorInformation.Cache.Level,(int)entry.ProcessorInformation.Cache.Size);
scrollablePanel.Controls.Add(entryForm);
scrollablePanel.Controls.Add(entryForm);
}
}
}
catch (Win32Exception exception)
{
CriticalError(exception.Message);
}
catch (InvalidOperationException exception)
{
CriticalError(exception.Message);
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
MessageBox.Show(exception.ToString(),"Unknown Error",MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
private static void CriticalError(string message)
{
MessageBox.Show(message,"Critical Error",MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
private void ScrollablePanel_SizeChanged(object sender,EventArgs e)
{
if (sender is not FlowLayoutPanel) return;
var panel=sender as FlowLayoutPanel;
foreach (var entry in panel!.Controls.OfType<CacheEntry>())
{
entry.Width=panel.Width-entry.Margin.Horizontal;
}
}
}
}
Code language: C# (cs)
Leave a Reply